The objective is to describe how to perform method for determination of saponification value
Procedure:
-
-
Saponification Value:
-
The Saponification value is the number that expresses in milligrams the quantity of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids and to saponify the esters present in 1 g of the substance.
- Reagent:
- 5 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide: Dissolve 3 g of potassium hydroxide in 5 mL of water and add sufficient aldehyde-free ethanol (96%) to produce 100 mL. Allow the solution to stand for 24 hours and decant the clear solution.
- Phenolphthalein solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of phenolphthalein in 100 mL of aldehyde-free ethanol (96%)
- 5 M hydrochloric acid: Dilute 4.25 mL of hydrochloric acid with sufficient water to produce 100 mL
- Procedure:.
- Place about 2 g of the test substance, to be examined or the quantity specified in the monograph into a 250 ml glass flask fitted with a reflux condenser.
- Add 25.0 ml of 0.5 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide and a few glass beads.
- Attach the condenser and heat under reflux for 30 min, or the time specified in the monograph.
- Add 1 ml of phenolphthalein solution R1 and titrate immediately (while still hot) with 0.5M hydrochloric acid (n1 ml of 5 M hydrochloric acid).
- Carry out a blank test under the same conditions (n2 ml of 5 M hydrochloric acid).
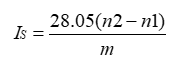
Where:
IS= Saponification Value
n2= End point of blank
n1= End point of test
m= weight in g of substance