- Reagent:
-
-
- Iodine Bromide Solution: Dissolve 20 g of iodine bromide in glacial acetic acid and dilute to 1000 mL with the same solvent.
- Potassium iodide: Dissolve 80.0 g of Potassium iodide in 1000 mL of water
- 1 M sodium thiosulfate: Dissolve 25 g of sodium thiosulfate and 0.2 g of sodium carbonate in sufficient carbon dioxide-free water to produce 1000 mL.
- Starch: Triturate 1.0 g of soluble starch with 5 mL of water and whilst stirring pour the mixture into 100 mL of boiling water
- Carbon tetrachloride reagent
-
| Iodine value II | Quantity of sample (grams) |
| Less than 20 | 1.0 |
| 20-60 | 0.5-0.25 |
| 60-100 | 0.25-0.15 |
| More than 100 | 0.15-0.10 |
(Table 1)
- Procedure:.
- Place a quantity of the test substance, accurately weighed, as specified in the monograph in a dry 300-mL to 500-mL stoppered The quantity of test substance used for the determination depends on the expected value as per table 1
- Add 15 mL of carbon tetrachloride and dissolve.
- Add 25 mL of iodine bromide TS, insert the stopper, previously moistened with potassium iodide (80 g/l) TS, shake the flask gently, and keep in the dark for 30 minutes, unless otherwise specified in the monograph
- Add 20 mL of potassium iodide (80 g/l) TS and 150 mL of water, and, whilst shaking the contents of the flask, titrate with sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/l) VS, adding starch TS as indicator towards the end of the titration.).
- Carry out a blank test under the same conditions (n2 ml of 0.1 M sodium thiosulphate).
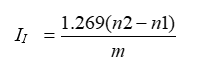
Where:
II= Iodine Value
n2= End point of blank
n1= End point of test
m= weight in g of substance